The position of most of the mainland in the belt of a desert and semi-desert tropical climate determines the weak development of surface runoff, both external and internal. In terms of total annual runoff (350 / km2), Australia is in last place among other continents. Almost over its entire area, the runoff layer is about 50 mm per year. The runoff layer reaches its greatest values (400 mm and more) on the windward moist slopes of the East Australian mountains. 60% of the mainland area is deprived of runoff to the ocean and has only a rare network of temporary streams (creeks).
]]>
 ]]>
]]>
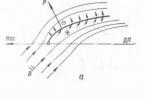
 The densest network of screams is in the Central Basin, they are much smaller in the Western Plateau. Water appears in them only after episodic downpours; they often end in drainless basins, which in the pluvial epochs of the Quaternary period were large freshwater lakes fed by the waters of large permanent rivers. Now these lakes have almost dried up, their baths are occupied by salt marshes. Even the largest drainless lake in Australia, Air, in the dry season is covered with a crust of salt up to 1 m thick, and in the rainy season (summer) it spills over an area of up to 1500 km2. The channels of the longest creeks in Australia, Cooper Creek and Diamantina, end at the shores of the lake.
The densest network of screams is in the Central Basin, they are much smaller in the Western Plateau. Water appears in them only after episodic downpours; they often end in drainless basins, which in the pluvial epochs of the Quaternary period were large freshwater lakes fed by the waters of large permanent rivers. Now these lakes have almost dried up, their baths are occupied by salt marshes. Even the largest drainless lake in Australia, Air, in the dry season is covered with a crust of salt up to 1 m thick, and in the rainy season (summer) it spills over an area of up to 1500 km2. The channels of the longest creeks in Australia, Cooper Creek and Diamantina, end at the shores of the lake.

The marginal regions of Australia have a runoff to the Indian Ocean (33% of the runoff from total area mainland) and to the Pacific. Rivers that empty into the ocean tend to be short, with steep dip profiles, especially those that drain from the East Australian Mountains. The volume of runoff, as well as the regime of river levels, is different and significantly depends on the amount of precipitation and the time of its occurrence. The rivers that start in the East Australian mountains (Burdekin, Fitzroy, Burnett, and others) are the most full-flowing and uniform in flow. The least full-flowing and unstable rivers of the western coast (Fortescue, Gascoigne, etc.), flowing from semi-desert coastal plateaus. Surface runoff is completely absent on the Nullarbor karst plain adjacent to the Great Australian Bight. Australia has only two major rivers, the Murray and the Darling. Starting in the Australian Alps, Murray is the most abundant river in Australia (basin area 1072 thousand km2, length 1632 m). Its food is mainly rain and, to a lesser extent, snow. Flowing with a barely noticeable slope through the vast southeastern plains of the Central Lowland, the river loses a lot of water to evaporation and barely reaches the ocean. At the mouth it is blocked by sand bars. The main tributary of the Murray is the Darling River, the longest river in Australia (the basin area is 590 thousand km2, the length is 2450 m), but it is even less full-flowing, and in dry seasons its waters, lost in the sands, do not reach Murray.

Available in significant numbers. Groundwater accumulates in artesian basins occupying the ancient troughs along the edges of the Western Plateau and in the Central Lowland. The aquifers are mainly Mesozoic sediments, the dense Paleozoic rocks are water-resistant. Groundwater is fed mainly due to precipitation.
Groundwater in central parts basins occur at great depths (up to 20 m, in some places up to 1.5 km). When they often come to the surface under natural pressure. The largest underground water basin Australia is called the Great Artesian Basin. It covers almost the entire Central Lowland from the Gulf of Carpentaria to the middle reaches of the Darling River. The pool has the largest number artesian wells that provide mineralized water, sometimes warm and even hot. In the semi-desert and desert regions of Australia, artesian basins are of great importance. But due to the mineralization of water, they are used not so much for the needs of industry and transport, and mainly for creating reservoirs in pastoral areas (in southern Queensland, in New South Wales and Victoria) . The quality of groundwater in Russia is regulated with.
Australia is the smallest of the continents
 Geographic location and size. Australia is the smallest of the continents, entirely located in the Southern Hemisphere. Its area is 7.6 million km2. Geographical coordinates extreme points mainland:
Geographic location and size. Australia is the smallest of the continents, entirely located in the Southern Hemisphere. Its area is 7.6 million km2. Geographical coordinates extreme points mainland:
northern - Cape York - 10 ° S, 143 ° E d.
South - Cape Yugo-Vostochny - 39 ° S, 146 ° E
Western - Cape Steep Point - 26 ° S, 113 ° E d.
Eastern - Cape Byron - 28 ° S, 153 ° E
Oceans and seas surrounding the mainland. The Australian mainland is characterized by compactness and low dissection. Only two large bays: Carpentaria - in the north and the Great Australian - in the south protrude deep into the coast.
Australia is washed by the warm waters of the Indian and Pacific oceans. In the Coral Sea, which washes the mainland from the northeast, there are temperature conditions favorable for the growth of corals. Here is the world's largest coral reef - the Great Barrier Reef.
From the history of exploration and development of Australia. Australia was discovered by Europeans later than all inhabited continents. The Dutchman Abel Tasman in 1643 rounded Australia from the west, proving that Australia is an independent mainland, and not part of an unknown southern mainland, as was previously believed. Exploration of the east coast of Australia belongs to the famous English navigator James Cook.
 From the end of the XVIII century. the development of Australia began by Europeans, who were attracted here by good pastures suitable for raising livestock. And when the richest gold deposits were discovered in Australia, a stream of “adventurers” poured in here, and England declared the entire mainland its colony.
From the end of the XVIII century. the development of Australia began by Europeans, who were attracted here by good pastures suitable for raising livestock. And when the richest gold deposits were discovered in Australia, a stream of “adventurers” poured in here, and England declared the entire mainland its colony.
Relief and minerals. At the base of the mainland lies the Australian platform. Along the eastern coast stretch low mountains of ancient folding - the Great Dividing Range. The western part of the mainland is occupied by a low plateau composed of igneous rocks. There are deposits of ore minerals, in particular gold. To the east, the plateau passes into the Central Lowland, covered with a thick layer of sedimentary deposits. Oil and gas deposits are found here - minerals of sedimentary origin. Oil is also produced in the south of the mainland - in the shelf zone. Australia is also rich in coal, deposits of which are found in the southeast of the mainland in sedimentary rocks.
Australia is the only continent that does not have active volcanoes and modern glaciation.
Climate. Australia has a hot dry climate with large annual and daily temperature fluctuations. That is why most of the mainland is occupied by deserts.
 Australia is located in three climatic zones. In the north of the mainland, a subequatorial climate dominates. In summer, equatorial air masses prevail here, due to which hot, humid weather is established. In winter, due to the movement of the zenithal position of the Sun, the high pressure zone also shifts to the north. Now dry tropical air masses dominate in the subequatorial belt. Therefore, there is little rainfall.
Australia is located in three climatic zones. In the north of the mainland, a subequatorial climate dominates. In summer, equatorial air masses prevail here, due to which hot, humid weather is established. In winter, due to the movement of the zenithal position of the Sun, the high pressure zone also shifts to the north. Now dry tropical air masses dominate in the subequatorial belt. Therefore, there is little rainfall.
Two types of climate are formed in the tropical belt - tropical dry in the west and in the central part and tropical humid in the east. Here, the eastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range are under the influence of moist air masses coming from Pacific Ocean. Saturation of air with moisture increases under the influence of warm ocean currents.
In the subtropical zone, three types of climate can be distinguished: in the southwest - a subtropical Mediterranean climate with dry summers and relatively wet winters (damp western winds of temperate latitudes prevail here in winter). The southeast of the mainland is characterized by a humid subtropical climate, which is formed under the influence of humid Pacific air masses and the warm East Australian Current. The area of subtropical continental climate is characterized by low rainfall throughout the year and sharp annual and daily temperature fluctuations.
Land waters. The rivers of Australia are shallow. The largest river system, the Murray, with a large tributary, the Darling, originates in the Great Dividing Range, where there is a lot of rainfall. Basically, for the inner desert parts of the mainland, drying rivers are characteristic, which are called screams here. Water appears in them only after rains. Water major rivers are used for land irrigation. For this, reservoirs were built on them. Lake Eyre, Australia's largest lake, lies 12 meters below sea level. Its water is salty.
Inland waters of Russia
 Inland waters make up numerous rivers, lakes, swamps, groundwater, glaciers, artificial reservoirs, reservoirs, ponds, channels.
Inland waters make up numerous rivers, lakes, swamps, groundwater, glaciers, artificial reservoirs, reservoirs, ponds, channels.
According to the well-known expression of Voeikov, a river is a product of the climate of its basin. Inland waters are also closely related to other components of nature. The territory of our country is very vast, and therefore the rivers of Russia (there are 420 thousand rivers over 10 km long) are very different in terms of flow volume, food sources and regime.
The rivers of Russia belong to the basins of the Atlantic, Pacific and Arctic Oceans and to the internal drainless Aral-Caspian region. Most of the rivers in Russia freeze in winter, have a mixed supply, mainly snow and rain, and are distinguished by a calm, flat flow. It is this river that is the Volga, the longest river in Europe, which has become a kind of symbol of Russia. Close in meaning to her are the Rhine for Germany or the Seine for France. But the fundamental difference between the Volga and similar rivers in other countries is that it flows into the endorheic Caspian Sea. Perhaps this is also due to the isolation of the Russian state, the inwardness of Russian culture, the tendency to the traditional way of life.  The amount of water in the river varies depending on the sources of food. Fluctuations in its level create a certain regime of the river.
The amount of water in the river varies depending on the sources of food. Fluctuations in its level create a certain regime of the river.
Rivers predominantly fed by snow are distinguished by a sharp increase in runoff and a rise in the water level in the river during the snowmelt period. In most parts of the country the rivers have a spring. In the northern regions, the snow melts intensively only at the beginning of summer, so here the rivers have a summer flood.
In winter, almost all rivers are covered with ice, winter low water comes.
Rivers with a significant share of glacial nutrition are characterized by an increase in runoff in summer, when ice melts.
The rivers of predominantly rain-fed have a flood regime. Unlike floods, floods can occur at any time of the year.
The longest and most abundant rivers flow into the Arctic Ocean: the Northern Dvina, the Pechora, the Ob with the Irtysh, the Yenisei - the most full-flowing river, the Lena - the longest river, the Indigirka, the Kolyma, etc. The Pacific Ocean includes the Amur, Anadyr, Penzhina, etc. .to the seas Atlantic Ocean such large rivers as the Don, Kuban, Neva carry their waters.
Thanks to the creation of artificial reservoirs on many rivers, the movement of large river vessels and the creation of powerful hydroelectric power stations became possible.
 Significant water reserves are concentrated in lakes. The largest lakes in Russia are the Caspian, Ladoga, Onega, Baikal.
Significant water reserves are concentrated in lakes. The largest lakes in Russia are the Caspian, Ladoga, Onega, Baikal.
The Caspian Lake is the largest lake in the world in terms of area, and Baikal is the deepest.
The lakes are distributed unevenly throughout the country. There are especially many of them in the Vilyui basin, on the West Siberian Plain and in the north-west of the East European Plain - in Karelia. These areas are in conditions of excessive moisture.
In the steppe and semi-desert zones, the climate is arid, so the number of lakes here is sharply reduced.
Lakes differ in the origin of the basins. There are tectonic, glacial-tectonic, thermokarst, dammed, estuary, artificial lakes.
Geographic location and size. Australia is the smallest of the continents, located entirely in the Southern Hemisphere. Its area is 7.6 million km2. Geographical coordinates extreme points of the mainland: northern - Cape York - 10 ° S, 143 ° E. southern village - Cape Yugo-Vostochny - 39 ° S, 146 ° E western - Cape Steep Point - 26 ° S, 113 ° E East - Cape Byron - 28°S, 153°E Oceans and seas surrounding the mainland. The Australian mainland is characterized by compactness and low dissection. Only two large bays: Carpentaria - in the north and the Great Australian - in the south protrude deep into the coast.
Australia is washed by the warm waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. In the Coral Sea, which washes the mainland from the northeast, there are temperature conditions favorable for the growth of corals. The world's largest coral reef, the Great Barrier Reef, is located here.
From the history of exploration and development of Australia. Australia was discovered by Europeans later than all inhabited continents. The Dutchman Abel Tasman in 1643 circled Australia from the west, proving that Australia is an independent mainland, and not part of an unknown southern mainland, as was previously believed. Exploration of the east coast of Australia belongs to the famous English navigator James Cook.
From the end of the XVIII century. the development of Australia began by Europeans, who were attracted here by good pastures suitable for raising livestock. And when the richest gold deposits were discovered in Australia, a stream of “adventurers” poured in here, and England declared the entire mainland its colony.
Relief and minerals. At the base of the mainland lies the Australian platform. Along the eastern coast stretch low mountains of ancient folding - the Great Dividing Range. The western part of the mainland is occupied by a low plateau composed of igneous rocks. There are deposits of ore minerals, in particular gold. To the east, the plateau passes into the Central Lowland, covered with a thick layer of sedimentary deposits. Oil and gas deposits, minerals of sedimentary origin, have been found here. Oil is also produced in the south of the mainland - in the shelf zone. Australia is also rich in coal, deposits of which are found in the southeast of the mainland in sedimentary rocks.
Australia is the only continent without active volcanoes and modern glaciation.
Climate. Australia has a hot dry climate with large annual and daily temperature fluctuations. That is why most of the mainland is occupied by deserts.
Australia is three climatic zones. In the north of the mainland, a subequatorial climate dominates. In summer, equatorial air masses prevail here, due to which hot, humid weather is established. In winter, due to the movement of the zenithal position of the Sun, the high pressure zone also shifts to the north. Now dry tropical air masses dominate in the subequatorial belt. Therefore, there is little rainfall.
Two types of climate are formed in the tropical belt - tropical dry in the west and in the central part and tropical humid in the east. Here, the eastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range are under the influence of moist air masses coming from the Pacific Ocean. Saturation of air with moisture increases under the influence of warm ocean currents.
In the subtropical zone, three types of climate can be distinguished: in the southwest - a subtropical Mediterranean climate with dry summers and relatively wet winters (damp western winds of temperate latitudes prevail here in winter). The southeast of the mainland is characterized by a humid subtropical climate, which is formed under the influence of humid Pacific air masses and the warm East Australian Current. The area of subtropical continental climate is characterized by low rainfall throughout the year and sharp annual and daily temperature fluctuations.
Land waters. The rivers of Australia are shallow. The largest river system, the Murray, with a large tributary, the Darling, originates in the Great Dividing Range, where there is a lot of rainfall. Basically, for the inner desert parts of the mainland, drying rivers are characteristic, which are called screams here. Water appears in them only after rains. The waters of large rivers are used for land irrigation. For this, reservoirs were built on them. Lake Eyre, Australia's largest lake, lies 12 meters below sea level. Its water is salty. natural areas. The flora and fauna of Australia is not rich, but very peculiar. Many species of plants and animals characteristic of this continent cannot be found in the nature of other continents of the Earth. Many types of eucalyptus trees are typical for Australia - from giants (more than 100 m high) to shrubs. Casuarinas with leafless thread-like branches are also found here. Of the endemic (found only on this mainland) animal species, one can name the platypus, echidna, kangaroo, and also the marsupial koala bear.
The central and western parts of the mainland are occupied by a zone of tropical deserts and semi-deserts. The subequatorial belt corresponds mainly to savannahs and light forests with red ferralitic and red-brown soils. Moist equatorial forests occupy small areas in the east and north of Australia. In the southeast and southwest of the mainland, landscapes of hard-leaved evergreen forests and shrubs on brown soils dominate.
Population. The vast majority (90%) of Australia's more than 21 million people are descendants of English and Irish settlers. Official language- English. The indigenous inhabitants of the mainland belong to the Australian race and are divided into numerous tribes, although their total number is small. The population density is highest in coastal areas in the east and southwest of the mainland. More than 90% of the population lives in cities.
The Commonwealth of Australia is the only state in the world that occupies the territory of an entire mainland. The state also includes the island of Tasmania and several small islands off the coast of the continent. The state has a developed economy, which was facilitated by both natural and historical factors. The capital is Canberra.
"Mainland Australia" - The population of Australia. Geography lesson in 7th grade. In Australia, cattle are bred in large quantities, as well as sheep. Australia. Australia is the most sparsely populated continent. Most important industry, traditionally, is agriculture. Modern population Australia is about 20 million people (!).
"Animals of Australia" - The length of the jump reaches 10 m. Animal world Australia. Ostrich Emu. Koalas live in trees in the eucalyptus groves of Eastern Australia. Australia. The platypus is a strange animal. Kangaroos live only in Australia. Wombat.
"Australia Lesson" - Practical work "Geographical position of Australia". . Australia is located in 3 climatic zones: subequatorial, tropical and subtropical. History of the discovery of Australia. Lesson topic: Geographical position of Australia. Luis Vaesa Torres. James Cook. Mainland - relics - animals and plants.
"Australian Union Geography Lesson" - The Commonwealth of Australia is a highly developed state. What is the level and pace of urbanization of the territory? History of Australia and Oceania. Melbourne - the capital of Australia in 1901-1927. - The 2nd largest city in the country. Thanks to James Cook, Australia became the property of England. Justify the answer. 3rd level.
"Geographical position of Australia" - Comparison geographical location Africa and Australia; identification of similarities and differences. Make a conclusion about the influence of geographical location on the nature of the mainland. Task number 2: designate the elements of FGP on contour map. Australia. General learning skills How to make a comparison. Practical work. The main area of the mainland is occupied by …
"The population of Australia" - Scientists suggest that the Aborigines came to the mainland from Africa. Adelaide. Aborigines belong to the Negroid - Australoid race. The most important industry, traditionally, is agriculture. Landmark of the city is the house of James Cook. The most densely and sparsely populated areas of Australia. . Flag.
In total there are 14 presentations in the topic
331. Determine which of the following rivers flow into the area of internal flow?
A) Yangtze, Huang He, Cupid.
C) Indus, Ganges, Tigris.
C) Danube, Dnieper, Vistula.
D) Ob, Yenisei, Lena.
E) Amu Darya, Volga, Or.
332. Determine the largest state in Eurasia by area.
C) Kazakhstan.
D) Saudi Arabia.
E) Russia.
333. Determine the driest region of Africa
A) Jungle.
B) sugar
C) Madagascar.
D) Savannah.
E) All the mountains of Africa.
334. Find where snow occurs in Africa.
a) There is no snow in Africa.
C) Only in the far north.
C) Only in the extreme south.
D) high mountain peaks.
E) In winter, snow falls everywhere.
335. Name the longest river in Africa.
C) Limpopo.
D) Amazon.
336. Identify the largest river in Africa.
A) Congo.
C) Limpopo.
D) Amazon.
337. Determine which basin most of the rivers in Africa belong to.
A) Atlantic.
B) Indian.
C) Quiet.
D) the Arctic.
E) internal drain.
338. Identify the largest waterfall in Africa and one of the largest waterfalls in the world.
A) Angel.
B) Niagara.
C) Iguazu.
D) Victoria.
E) There are no waterfalls in Africa.
339. Determine which of the following rivers are most used for irrigation in Africa.
A) Congo, Limpopo.
B) Niger, Neil.
C) Orange, Zambezi.
D) Boats, Zaire.
E) In Africa, rivers are not used for irrigation.
340. Identify the largest river in Africa that flows into the Indian Ocean.
A) Zambezi
B) orange.
C) Senegal.
E) Limpopo.
341. Determine the main source of food for the rivers of Africa.
A) Glacial and snowy.
B) rain.
C) With water from swamps.
D) underground water.
E) Water from the oceans and seas.
342. Which of the largest rivers in Africa crosses the equator twice?
B) Congo (Zaire).
D) Zambezi.
E) Senegal.
343. Which part of Africa has the most lakes?
A) in South Africa.
B) in West Africa.
C) in North Africa.
D) East Africa.
E) There are no lakes in Africa.
344. The largest lake in Africa by area:
A) Victoria.
C) Tanganyika.
E) Rudolf.
345. What is the most deep lake Africa?
A) Victoria.
C) Tanganyika.
E) Rudolf.
346. Determine which state in Africa is the largest in area:
C) Sudan.
E) Ethiopia.
347. Identify the saltiest areas indian ocean.
A) the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf.
C) the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
C) The coast of the islands of Sumatra and Java.
D) West Coast Australia.
E) East Coast islands of Madagascar.
348. In which part of the Indian Ocean are the most fossil fuels found today?
A) in the Red Sea.
C) in the Java Trench.
C) In the Central Indian Basin.
D) Off the coast of Africa
E) in the Persian Gulf.
349. In what part of the Indian Ocean are sea ice and icebergs?
A) North.
B) South.
C) Eastern.
D) Western.
E) central.
350. What is the driest continent on earth?
A) Eurasia.
B) Africa.
C) North America.
D) South America
E) Australia.
351. In what century did the gradual discovery of Australia take place?
A) In the XV - XVI centuries.
B) XVI-XVII centuries.
C) In the XVII - XVIII centuries.
D) In the XVII - XIX centuries.
E) XIX - XX centuries.
352. What a great geographical feature in Australia named after the Dutch navigator Abel Tasman?
A) mainland.
E) an island.
353. Determine after the study of which navigator it was proved that Australia is an independent mainland:
A) A. Tasman.
B) V. Torres
C) J. Cook.
D) A. Krusenstern.
E) F. Bellingshausen.
354. What part of Australia has volcanoes?
A) North.
C) Eastern.
D) Western.
E) There are no volcanoes in Australia.
355. In what part of Australia are modern glaciers found?
A) North.
C) Eastern.
D) Western.
E) There is no modern glaciation in Australia.
356. What is the climate in Australia?
A) Humid equatorial.
C) dry tropical.
C) Humid tropical.
D) Moderately humid.
E) Moderately sharply continental.
357. What part of Australia is located in the subequatorial zone?
A) North.
C) Eastern.
D) Western.
E) central.
358. Summer in the northern part of Australia is very humid, what months does it occur in?
A) December - February.
Introduction
Australian Union
Introduction
Australia is the smallest, driest and sparsely populated continent on our planet. There are many unusual things for us here: when moving north it gets hotter, and south it gets colder. There are especially many plants and animals that cannot be found on other continents. Australia is entirely in the Southern Hemisphere (from the Latin austral - opposite, southern). On the mainland, the island of Tasmania and small islands, there is only one state - the Commonwealth of Australia. The capital is the city of Canberra.
Geographical position. Discovery history. Relief and minerals
The coasts of Australia, like those of Africa, are very slightly indented. There are few bays here, the most convenient of them are located in the southeast of the mainland, where large ports are located. More indented coastline north coast. Australia is washed by the warm waters of the Indian and Pacific oceans. Temperature conditions promote the growth of corals, which form calcareous structures of bizarre shape. Therefore, along the northeastern part of Australia, as if repeating the outlines coastline, stretches for more than 2 thousand km, the world's largest coral reef, called the Great Barrier Reef.
Australia was discovered by Europeans later than other inhabited continents. The discovery was hindered by its remoteness from Europe and isolation. Even ancient scientists assumed that there was land south of the Southern Tropic. This land was discovered by the Dutch. In the first half of the XVII century. they already knew almost all the northern, western and southwestern coasts of the mainland. Of great importance for the knowledge of Australia was the expedition of the Dutch navigator Abel Tasman. He explored the northern and northwestern shores of the mainland and discovered in 1642 an island later named after him - Tasmania.
The east coast of Australia was discovered in the second half of the 16th century. the largest English navigator and explorer J. Cook. As a result of Cook's research, the legend of the existence of a large southern continent was finally rejected and it was proved that Australia is an independent continent, and not part of the unknown Antarctic continent, as previously thought.
From the end of the 18th century Australian exploration begins. The British government first exiled criminals to Australia, as a result of which the city of Sydney arose in the southeast of the mainland as a colony of convicts.
The attention of Europeans in Australia was also attracted by good pastures that could be used for raising livestock. Therefore, the study of the interior of the mainland began with the search for pastures and water for the cattle of European settlers. In connection with the discovery of the richest gold deposits in the middle of the XIX century. many “seekers of happiness” rushed to Australia. England declared the entire mainland its colony.
The relief of Australia, like Africa, is relatively simple. It is based on the Australian platform. In the east of the mainland there are heavily destroyed, low mountains of ancient folding - the Great Dividing Range. Faults and river valleys divide the mountains into separate massifs. Their tops, as a rule, have a domed shape. The eastern slopes of the mountains drop steeply to the sea, the western slopes are more gentle. In the extreme southeast, the mountains reach their highest height. IC to the west, the surface drops and the mountains pass into the Central Lowland, which is covered with a thick layer of sedimentary deposits.
The western part of the mainland is uplifted. There is a vast plateau with a height of 400-600 m, on which low, bizarrely shaped mountains rise in some places, their foot "drown" in rubble and sand. Australia is the only continent where there are no active volcanoes and modern glaciation.
In the process of development, the continent experienced uplifts, subsidences and faults. As a result of deflections and faults, a significant part of the land sank to the bottom of the Pacific Ocean, the islands separated New Guinea and Tasmania.
Australia is rich in all the main minerals necessary for the development of industry and agriculture: coal, the deposits of which are found mainly in the southeast of the mainland in sedimentary rocks, and various ores. There is also oil and natural gas.
Climate
You already know that most of Australia is located in the tropical zone, so a tropical dry climate prevails there. Only 1/3 of the territory receives sufficient or excessive rainfall. Australia has higher temperatures and less rainfall than South Africa. What explains this? A significant length of the mainland from west to east, due to which continental air masses are formed in Australia. The low height of the mainland above sea level is also important.
How is precipitation distributed on the mainland? To do this, you can look at the climate map and find out by conventional signs how much and where precipitation falls. But in order to explain the reasons for the distribution of precipitation, it is necessary to remember what air masses, what winds prevail in each climate zone. Northern Australia is located in the subequatorial belt, a subequatorial climate is formed here, as well as a similar climate in Africa. You know the formation of a dry tropical climate. In the east of the tropical and subtropical zones there are areas of humid climate. The eastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range are all year under the influence of maritime air masses coming from the Pacific Ocean. Saturation of air with moisture increases under the influence of warm ocean currents. Therefore, heavy rainfall falls on the slopes of the mountains. The south of the mainland is in the subtropical zone.
There are no large full-flowing rivers in Australia. More than half of the area of the mainland has no flow into the ocean. The inner desert and semi-desert parts of the mainland are characterized by a network of temporary drying rivers - screams. Full-flowing rivers throughout the year are located only in the east of Australia, where there is a lot of rainfall. The food near the rivers, of course, is only rain and from groundwater.
Australia's largest river system is the Murray, with a major tributary, the Darling. These rivers originate in the Great Dividing Range. In the lower reaches of the Darling, during a drought, it dries up and breaks up into separate reservoirs. Murray does not dry out, but its level changes dramatically. During the rains, the river overflows strongly over a flat plain. High water on the Murray usually comes on quickly and does not last long.
Due to the sharp fluctuations in the water level on Murray and Darling, navigation is difficult on them. River waters are used to irrigate fertile but arid lands. For this, reservoirs were built on them.
Most of Australia's lakes do not have a runoff and are saline. Many lakes are filled with water only during the wet period. The largest of them is Lake Eyre, lying 12 m below sea level. During the rains, the screams flowing into the lake bring a lot of water, it overflows, and its area greatly increases. In the dry season, Eyre breaks up into shallow reservoirs, the dried-up areas are covered with a crust of salt.
The lack of surface water is partly compensated by the large reserves of groundwater that accumulate in artesian basins. Artesian waters contain quite a lot of salts.
natural areas. The peculiarity of the organic world
If you compare the distribution of the natural zones of Australia and Africa, you will find that in Australia, as well as in Africa, large area occupy zones of savannahs and tropical deserts. Tropical deserts and semi-deserts are located in the central and western parts of the mainland. Savannas border this zone from the north, east, southeast and southwest.
Although Australia has the same natural areas as South Africa with Madagascar, except for the regions of altitudinal zonation, but the organic world here is completely different. Nature has created a huge nature reserve in Australia, where many plants and animals are preserved, close to those that inhabited the Earth in ancient times and disappeared on other continents. The species composition of plants and animals is characterized by poverty and originality. This is due to the fact that Australia and the adjacent islands have long separated from other continents. The organic world has long developed in isolation. Up to 75% of mainland plant species are found only in Australia. These include many types of eucalyptus, which are very diverse. There are giant eucalyptus trees, more than 100 m high. The roots of such trees go 30 m into the ground and, like powerful pumps, pump moisture out of it. There are stunted eucalyptus trees and shrub eucalyptus trees. Eucalyptus trees are well adapted to dry climates. Their leaves are located with an edge to the sunlight, the crown does not shade the soil, so the eucalyptus forests are light. In eucalyptus trees, hardwood is a good building material. And their leaves are used for the production of oils, paints, medicines.
In addition to eucalyptus, Australia is characterized by acacias, casuarinas with leafless thread-like branches, which are not found on other continents.
In the subequatorial forests, among tall grasses, along with other trees (palms, ficuses, etc.), peculiar bottle trees grow - with a trunk thick at the base, sharply tapering upwards. A characteristic feature of subtropical forests is the dominance various kinds eucalyptus intertwined with vines, many tree ferns.
Thickets of dry shrubs are common in the interior desert regions, consisting mainly of low-growing prickly acacias and eucalyptus trees. Such thickets are called scrub. There is almost no vegetation on mobile sandy ridges and stony placers. Unlike Africa, there are no oases in Australia, but the deserts do not look as lifeless as, for example, the Sahara.
The fauna of Australia is also very peculiar. Only here live the most primitive mammals - echidna and platypus. They are interesting in that they hatch the young from eggs, and feed them with milk, like mammals. There are many marsupials in Australia. Their cubs are born very small, and the mother wears them in a bag representing a fold of skin on her stomach.
The vast majority of marsupial families are unique to Australia. Among them, the kangaroo family is especially common. Giant kangaroos reach 3 m. There are dwarf kangaroos, 30 cm in size. There are also wombats resembling marmots. In the eucalyptus forests, you can meet the marsupial koala bear. It lives in trees and leads a sedentary nocturnal lifestyle, it is also called the Australian sloth. A very rare predator, the marsupial devil, has survived on the island of Tasmania.
The world of birds is rich, diverse and also peculiar. Especially a lot of parrots. Found in the forests beautiful bird lyrebird, birds of paradise with bright plumage, in dry savannahs and semi-deserts - emu. There are lizards, poisonous snakes, crocodiles are found in the reservoirs of Northern Australia.
Australians love and care about the nature of their mainland. They pay much attention to the protection of plants and animals and their study. An emu and a kangaroo are depicted on state emblem countries, and echidna, platypus, lyrebird are depicted on Australian coins.
Australian Union
The modern population of Australia consists of an indigenous minority and immigrants, who now make up its bulk. The indigenous population of Australia - the Aborigines - belongs to the Negroid-Australoid race and has a dark brown skin color, wavy black hair, a wide nose, and strongly protruding eyebrows.
Scientists suggest that they came here from South-East Asia. Before the arrival of Europeans, Australians were at a very low level of development. The aborigines were not engaged in agriculture or cattle breeding, they did not know how to make fabrics, they did not know metals. They lived by hunting, gathering, well oriented in nature and led a nomadic lifestyle.
The alien population includes descendants of Europeans, almost exclusively English - Anglo-Australians who speak English.
About 19 million people live in Australia. Among other continents, Australia stands out for its very low population density. On the territory of the mainland, the population is distributed extremely unevenly. Almost all of it is concentrated on the eastern, southeastern, and partly southwestern margins of the mainland, where it is better natural conditions. The population here consists of Anglo-Australians. Inland Australia and the entire north are sparsely populated. Mostly Aboriginal people live here.
Before colonization, the entire population of the mainland were indigenous people. They were located in the east and southeast of Australia, where natural conditions are more favorable for human life. After the arrival of Europeans on the mainland and in connection with the development of sheep breeding, the indigenous people began to be pushed back into the interior of the mainland - to arid regions, dooming them to starvation. In addition, the Europeans brutally exterminated the Australians, killed them, poisoned food, water in wells. The number of indigenous people on the mainland dropped sharply from 310,000 to 50,000 people.
Aboriginal people lived in beggarly conditions on reservations (territories set aside for the forced settlement of indigenous people) located in desert areas. They were completely disenfranchised, had no right to live in cities, to participate in public life. The world-famous self-taught artist Namajira, whose paintings were highly valued in many countries, had no right to attend exhibitions of his works. Today Australian aborigines became legally equal citizens of their country. It is important that the natives have ceased to die out and their numbers continue to grow. Mixed marriages appeared, which did not exist before. Part of the natives work on farms as farm laborers as shepherds and workers. Others continue to live as semi-wandering hunter-gatherers. Australians make their dwellings from grass, branches and earth. The obtained food is divided by the elders equally among the members of the tribe. No preference is given to the hunter who killed the animal. Various rituals contribute to the education of honest, courageous, not afraid of difficulties members of the tribe.
The leading place in the economy of the Commonwealth of Australia belongs to industry, in which all sectors are well developed. Based on various minerals, a mining industry was formed here. The country is rapidly developing mechanical engineering, the chemical industry, as well as the food industry: butter-making, cheese-making, and the production of canned goods (dairy, meat, vegetables, fruits).
Agriculture is also well developed. Anglo-Australian farmers own large land plots. They use machinery, fertilizers, and hired labor, thanks to which they receive high yields and profits. Leading in agriculture belongs to pasture animal husbandry - sheep breeding. Australian merinos provide over half of the world's shearing. In areas with low rainfall, the main food for sheep is drought-resistant grasses and shrubs. Sheep here graze on natural pasture throughout the year. In the south-east of the country, sheep are grazed in areas sown with fodder grasses.
Many sheep farms are sparsely populated. As assistants, farmers use a specially bred breed of dogs - kelpies, which were brought in the last century from Scotland. Kelpie can replace three workers. She skillfully copes with the herd, but she will never hurt the sheep. Droughts, fires, and floods cause great damage to sheep breeding.
Cattle, mostly thoroughbred cows, are bred mainly in the north and east of the country, where there is sufficient rainfall.
Wheat occupies a leading place among agricultural crops. Wheat fields are located in the southeast and southwest of the country. On the coastal plains of the subequatorial and tropical parts of the country, pineapples, bananas, sugar cane, etc. are grown. Not far from major cities There are many orchards on irrigated lands.
In the economy of the country, the seas washing Australia are of great importance. They catch fish, breed pearl mollusks, edible oysters. Fishing for sea turtles. Australia has no land connections with other countries. All its cities, with a few exceptions, are the largest seaports. Through them, along with air communication, trade and cultural relations with countries of other continents are carried out.
The natives were very careful about nature. The nature of Australia has changed most rapidly and strongly since the colonization of the mainland and with further economic activity Anglo-Australians. Many animals have been exterminated as a result of hunting and changes in their living conditions. The densely populated eastern, southeastern and southwestern parts of Australia have been most heavily modified. Valuable tree species are cut down here. Significant areas cleared from the forest are used as pastures for dairy cattle.
In the past, dry woodlands and shrubs are now occupied by wheat fields, vineyards, and olive tree plantings.
The appearance of the arid, sparsely populated central and western parts of the mainland has also changed. The best plots are divided into rectangular squares, fenced with wire fences - pastures for livestock. In connection with the development of industry, automobile and railways, power lines. New species have appeared in the flora and fauna of Australia. Plants imported from Europe (poplar, oak, etc.) and animals, such as the wild dog dingo, rabbits, quickly settle, which suppresses the local organic world. Thus, rabbits and sheep contributed to a significant decrease in marsupials, since they used the same pastures.
Australians strive to preserve the uniqueness of the organic world. To this end, there are laws prohibiting the import of plants and animals, and the export of rare native species is also strictly controlled. To preserve natural complexes and save endangered rare plants and animals, a significant number of National parks and reserves.
List of used literature
1. “Geography of continents and oceans. Grade 7 ": textbook. for general education institutions / V.A. Korinskaya, I.V. Dushina, V.A. Shchenev. - 15th ed., stereotype. – M.: Bustard, 2008.