Quicksand is a very dangerous phenomenon, and you can get into them completely unexpectedly. There are beaches all over the world that turn into a risk zone at high tide. In the summer, you want to walk on the yellow sand, and all of a sudden it begins to sink in and grab your feet. And you have no way to get out. Panic begins!
How and where do they appear
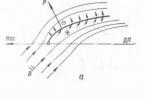
The condition for the formation of quicksand is a large source of water, located at a depth of one to ten meters. Such sources provoke shedding of sand. In most cases, they try to break out with great force, rising as close to the surface as possible and enveloping individual grains of sand with water.
Here's what it looks like schematically:
On the surface, a loose sandy mass impregnated with water is formed, which for some time retains its balance. But when any object hits it, the entire structure collapses, and physical forces try to return the displaced sand back. That is why suction occurs.
How to identify quicksand
It is sometimes impossible to determine the location of such sand. From above, it looks quite reliable, and there is no doubt whether it is possible to move on such a surface.
What to do to avoid getting into quicksand
- Take a stick with you!
When you go for a walk along the beach, take a large stick with you so that you can check the ground for quicksand.
Rules of conduct in quicksand
- Throw away everything you carried in your hands!
If you find yourself in quicksand, then try to throw away everything that was in your hands, such as a backpack.
Important: When going on such a walk, always wear light shoes, because, for example, boots will only increase the suction.
- Do not panic!
Try not to panic or make sudden movements. All active attempts to pull out, for example, a leg will form a rarefaction of air. A huge force will arise, which will drag the foot into the sand even more. Your ability to relax at this moment will depend on your life.
Surprising fact: The effort it takes to lift a foot out of quicksand can be compared to the weight of a car.
- Breathe deeply!
Deep breathing will help you stay calm and make you more buoyant.
- Lie on your back!
If you have sunk to the hip or higher, then bend back. The more you distribute your weight, the harder it will be to sink. Try to slowly and carefully release your legs. In this position, you can try to sort of swim on the sand. This way you can keep the balance certain time and wait for the arrival of rescuers who know everything about this phenomenon and actively monitor the coast in order to come to the rescue in time.
In this video you can see how to get out of the quicksand and bog:
// 0 Comments
Quicksand is a deadly attraction. The main danger lies in the fact that they are almost impossible to distinguish from ordinary sandy areas. This means that if you are traveling, for example, in the desert, where there is often the same type of landscape without stones and vegetation, then at some point there is a chance that you will simply start to fall "under the ground".
Quicksand: what is it
Basically, quicksands are formed in places where underground sources appear or when groundwater approaches the soil. In addition, the condition for their appearance is the presence of sand without clay impurities with a grain diameter of up to 3 mm.
The smallest particles of moisture, mixing with such sand, do not allow air to pass through, and the friction between the grains of sand disappears. As a result, the grains of sand turn into a semi-liquid mass, a swamp, which outwardly is almost impossible to distinguish from an ordinary desert or beach. It is a viscous mass with a huge reaction force.

How to spot quicksand
Visually detecting classic quicksand is difficult - they can lie in wait for a traveler anywhere along the entire path. There is a road that takes more than one day, gradually mindfulness becomes dull, which leads to serious consequences.
Since quicksand is a viscous quagmire, outwardly it looks like a flat surface with small motionless ripples. That is, any flat territory can potentially turn out to be an impassable swamp. It should be noted that sand can dry out on the surface of the bog and sometimes even grass grows on it.
Most often, quicksand can be found along the banks of reservoirs and in the lowlands of hills - where underground sources are likely to come to the surface. To make sure, you need to move slowly, be able to quickly get rid of the backpack and other cargo, as well as feel the road in front of you with a pole or stick.

In a normal, dry state, when pouring from vessel to vessel (let's take an hourglass as an example), sand passes air. But if there is moisture between the grains of sand, the air does not pass, and the sand does not spill out, clogging the passage. This property is the basis for the appearance of a quagmire.
Such a sandy is characterized by a huge counterforce. If a person's leg falls into quicksand, it is necessary to expend the effort of a heavyweight weightlifter to free it, and then, provided that his second leg has a reliable fulcrum and is on a solid surface.
In addition, the impact of a quagmire can be compared to a seat belt - the faster the trapped person moves, the stronger the swamp binds him. This is due to the momentary "solidification" of quicksand due to the appearance of rarefied air under the released foot. The presence of a discharged space leads to the opposite effect - tightening the leg even deeper ("collapse").
Quicksand vs. Man
At its core, quicksand can be attributed to a variety of non-Newtonian fluids with a high content of fine solids (grains of sand). That is why a person, getting into such a place, begins to fall into it, like into water. If at the same time he does not make sudden movements, then the dive will stop when the mass of the displaced sand becomes equal to the mass of a person.
What to do if you get caught in quicksand
There are certain rules of conduct when entering quicksand. Following these rules will allow you to get out of the situation alive.
1. Don't panic! If you start to twitch or make other sudden movements, you will go towards the core of the planet.
2. Fall on your back, flat, preferably on your back - in general, take a horizontal position with your whole body.
3. Try to immediately throw off everything superfluous - a backpack, a tent, etc. Life is more important.
If you start making sudden movements, pits will appear that will continue to suck. After the excitement has calmed down, move slowly, preferably back, in the direction from which you came, since it is not known how far the dangerous sands extend.
Relax your body, imagine that you are lying on your back in the water and relaxing. When moving, the sand should flow gently under the body and on the sides. This process is laborious, but effective. If your lower body does enter the sand vertically, place your torso on the surface and slowly but firmly release your legs.
Interesting and tragic facts about quicksand
Morecambe Bay, England. Known since the 15th century, when it was forbidden to enter the sand at high tide. Annually claimed the lives of up to 150 people. People who fell into quicksand died during a 9-meter high tide that covered them with their heads.
Goodwin Shoals at South Foreland, England. Devour the ships, the remains of which rise above the sands. The place is known as the "Ship Graveyard". One day, the Goodwin Shoals swallowed up the lighthouse tower.
Tarnagen Fjord, Alaska. The coast is about 80 km long and consists of quicksand.
Sable Island, Atlantic. Quicksand swallows entire ships after shipwrecks.
Jamaica, city of Port Royal. Completely drowned in quicksand in 1692. 2000 citizens died. After the earthquake, the soil hardened, so it was initially believed that the city was swallowed up by the “abyss of the sea”.
An example of hitting the quicksand of American paratroopers
quicksand
Quicksand, found in different parts of the globe, has always caused fear in people. It is generally accepted that this sand, which looks no different from the usual one nearby, is fraught with a mortal danger for anyone who steps on it. There are many stories about how these sands sucked their victims in until there was no trace of them. However, in reality, quicksand does not have such power. If you have an idea of \u200b\u200bwhat it is and how to behave correctly, then quicksand will not bring any harm.
Usually quicksand, or quicksand, appear near the mouth big rivers and on gentle coasts. These sands are formed due to the fact that under them there is a dense layer of clay that does not let moisture into the ground. This leads to the accumulation of rain and river water in the sand. The accumulating water dilutes the round grains of quicksand, and they seem to float in it. That is why they are not able to hold heavy objects on the surface.
Contrary to popular belief, people who get on quicksand do not drown in it at all. Since quicksand contains a lot of moisture, you can swim in them like in water. It is also important that quicksand is denser than water, and therefore it is easier to stay on the surface in it.
If you ever find yourself on quicksand, then remember to move slowly enough. This allows the sand to flow around your body, as it does when you swim in water. In this case, you can not be afraid for your life.
From the book The Newest Book of Facts. Volume 3 [Physics, chemistry and technology. History and archeology. Miscellaneous] author From the book The Complete Encyclopedia of Our Delusions author authorSinging Sands (According to V. Mezentsev) Dzhebel-Nakug (Bell Mountain) on the Red Sea has long been covered with legends. When a person climbs to its top, the sand seems to groan underfoot, In the bowels of this mountain, the inhabitants believe Sinai Peninsula, hidden
From the book 100 great records of the elements author Nepomniachtchi Nikolai NikolaevichThe most treacherous quicksand Alaska has a 60-kilometer-long fjord made up of quicksand. Found on different continents sea beaches, which at high tide turn into a sour mess, sucking everything in a row. stripes sandy beaches along the banks
From The Complete Illustrated Encyclopedia of Our Delusions [with transparent pictures] author Mazurkevich Sergey AlexandrovichQuicksand Quicksand, found in different parts of the world, has always caused fear in people. It is generally accepted that this sand, which looks no different from the usual one nearby, is fraught with a mortal danger for anyone who steps on it.
From the book 100 famous mysteries of nature author Syadro Vladimir Vladimirovich From the book Who's Who in the Natural World author Sitnikov Vitaly PavlovichWhat is quicksand? The infamous quicksand is sand with very fine grains of sand containing a large number of water. Heavy objects here very easily disappear from the surface, as if they are sucked in by sand. Unlike ordinary quicksand
From the book Historical districts of St. Petersburg from A to Z author Glezerov Sergey EvgenievichSands This was the name of the area occupied by the current Soviet (formerly Rozhdestvensky) streets, as well as Mytninskaya and Degtyarnaya streets crossing them, Suvorovsky, Grechesky and Ligovsky avenues. It was the highest part of the city that never
From the book The Complete Illustrated Encyclopedia of Our Delusions [with illustrations] author Mazurkevich Sergey AlexandrovichQuicksand Quicksand, found in different parts of the world, has always caused fear in people. It is generally accepted that this sand, which looks no different from the usual one nearby, is fraught with a mortal danger for anyone who steps on it.
From the book All About Everything. Volume 3 the author Likum ArkadyWhat is quicksand? In many places around the globe, people have lived in fear of quicksand for centuries. They were credited with the mysterious ability to suck in the victim until there was not a trace of it left on the surface of the earth. In fact, quicksand has no
From the book 100 Great Records of the Elements [with illustrations] author Nepomniachtchi Nikolai NikolaevichThe most insidious quicksand In Alaska there is a fjord 60 kilometers long, consisting of quicksand. On different continents, there are sea beaches, which at high tide turn into a muddy mess that sucks everything in a row. Stripes of sandy beaches along the shores From the book 3333 tricky questions and answers author Kondrashov Anatoly Pavlovich
What is quicksand and why is it dangerous? There are many cases when people became victims of the so-called quicksand. It is easy to see something mystical in the ability of ordinary-looking sand to suddenly swallow objects on its surface,
From the book Bulgaria. Guide by Shetar Daniela*Golden Sands A gently curved strip of golden sand, 4 km long and in some places more than 100 m wide, gave the name to the resort *Golden Sands (Zlatni Piasci) (10). The coast here is almost flat and forms a vast shallow water, and the sea is usually calm and completely devoid of currents, which
Nature is fraught with many dangers. Unfortunately, we sometimes underestimate these dangers. And such neglect leads to tragedy. There are places in nature where it is extremely dangerous to be. To such hazardous areas include quicksand.
What are they? This is a sandy surface, characterized by increased mobility. Any object or living being caught in the quicksand can be sucked in. The speed of tightening is uneven: it can happen both in a matter of minutes and over long months. Different nations have legends and myths associated with quicksand. The insidiousness of quicksand is that outwardly they seem quite safe. There are many legends about quicksand in English folklore, since there are many such danger zones in England.
This is not to say that people did not try to fight quicksand. In the 19th century in England, quicksand was carefully destroyed, filling them with stones, sand and rubble. Therefore, now there is practically no danger of meeting them in those places where people live. However, in some places, quicksand is still waiting for its victims. Surprisingly, there is no clear explanation for this phenomenon yet.
There are various hypotheses, certainly interesting ones. Russian physicist V. Frolov believes that the phenomenon of quicksand is based on electrical effects, due to which friction between the grains of sand decreases and the sand becomes viscous and fluid. Viscosity can spread to a depth of several meters, the ground becomes unsteady and sucks in any object or living being. There is an assumption that main reason The fact that sand draws various objects into itself is hidden in the form of individual grains of sand. All of them are of the correct spherical shape. That is why any heavy object sinks so easily, passing "through" them.
The American scientist J. Clark has been studying the phenomenon of quicksand for a long time. He believes that these sands are mixed with water, therefore they have acquired the properties of a liquid medium. Clark suggests that ripple is a special state of sand. It can manifest itself in different places if there is exposure to water. For example, if the surface is regularly flooded with water at high tide, or if there is an underground river under the surface.
In England, not far from Morecambe Bay, there is a place called Arnside. There are regular tides. At low tide, the water recedes for several kilometers, exposing the bottom of the bay. If you step on the sand, which seems very stable, you can immediately be pulled down. It is impossible to escape on your own, so many die.
It belongs to the dangerous and very a nice place- Tarnagen Fjord in Alaska. It is also not recommended to be there during low tide. Many people know about the island called Sable. He is in Atlantic Ocean 180 kilometers from the coast of Canada. There are many reefs in its vicinity, which are often the cause of shipwrecks. The remains of the broken ships on the shore are covered with sand.
There are many quicksands not only in Alaska, but also in the Sahara. It is known that entire caravans can sink into the sand in the desert. Scientists have found that there is an underground river under the Sahara, which may be why the surface becomes so insidious.
Quicksand is dangerous not only for an individual person or animal. Can go underground whole city. This is exactly what happened in 1692 in Jamaica. A whole area of the city of Port Royale was drawn into the quicksand. The city was on a sandy surface, which is why the tragedy happened. On June 7, 1692, an earthquake struck. Historical chronicles tell how some residents of the city immediately fell into the ground, others were sucked up to the knee or to the waist. The earthquake lasted several minutes. Then the sand immediately turned into a solid mass that held people in its captivity. Many died. In the 19th century, on the site of the lost city, the remains of the walls of collapsed houses were still visible, and in 1907, after another earthquake, everything went underground.
> wilderness survival > coastal quicksand
Why are coastal quicksands dangerous?
Coastal quicksands are found on the shores of lakes, rivers, seas, where rising springs often come across. On top of quicksand, there may be a thin crust of silt formed from a fine fraction of sand. From the point of view of physics, the explanation for quicksand is very simple and depends on the ratio and interaction of sand and water. Sand grains are enveloped in water, and a film forms around them. There is air between the grains of sand, but with an increase in the amount of water, the air is displaced, and a mixture of sand and water is formed, the properties of which differ significantly from the mixture of sand, water and air.
The main condition for the formation of coastal quicksand is a large source of water, which is located at a depth of several meters, and sometimes several tens of meters. Such sources provoke shedding of sand. In most cases, they try to break out with great force, rising as close to the surface as possible and enveloping individual grains of sand with water. Thus, a loose sandy mass impregnated with water is formed, which for some time retains its balance. When any object hits here, the structure collapses, and physical forces try to push back the displaced sand. Suction occurs. Naturally, not any source can become the basis for the formation of quicksand. Only a source that moves in an inclined horizontal direction or almost vertically becomes the culprit in the formation of a coastal "trap".
It is sometimes impossible to determine the location of such sand. From above, it looks quite reliable and there is no doubt that you can move on this surface. Grass and flowers can grow here, however, if there is a similar sand formation in a rocky area, it is better to bypass it. It is simply impossible to check whether a nearby source of water provoked the appearance of quicksand.

The danger of the coastal sands is perhaps even greater than the danger of the swamp. When you walk through the swamp, you always understand the situation and realize where you are. And the coastal sand in appearance is no different from an ordinary beach, but at the same time it can become deadly.
How to get out of coastal quicksand
Hit and death of people in quicksand, not such a rarity. Why is it so difficult or almost impossible to get out of the whirlpool of sand? The fact is that it is very viscous, so any sudden movements cause even more resistance, despite the fact that the density of quicksand is only one and a half times greater than the density of water. You can get out of the elements only if you move very smoothly, or even better, try to lie on your back or stomach with your legs free, and try to "swim" on the sand in the direction you came from. If you cannot move forward, do not make sudden movements, call for help. Get rid of unnecessary things and clothes as much as possible. If there is a person nearby who can help you, let him not get too close, he will have to give you a rope, stick or other object, for which you will need to cling tightly and climb slowly but surely. Without additional emphasis, it is almost impossible to get out on your own. When you try to pull, for example, a leg, a vacuum is formed and a huge force arises, pulling the leg back. The force that must be applied to lift the leg can reach several hundred kilograms.